
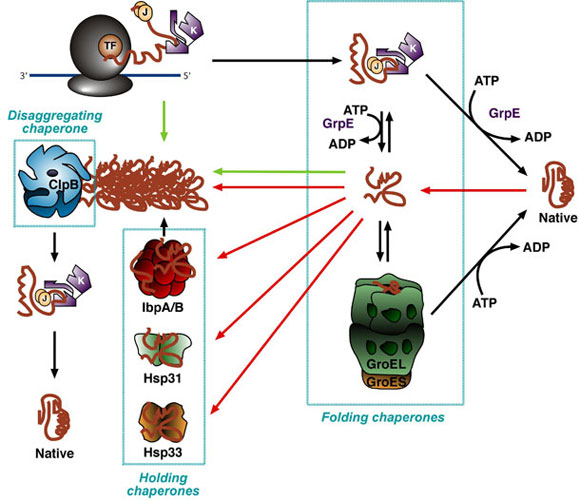
Repeated cycles of hsp binding and release help the target protein to refold. After the hsp40 dissociates, the rapid rebinding of ATP thus, induces the dissociation of the hsp70 protein after ADP release. This cause the hsp70 molecules to bind more tightly with the target. Aided by a set of smaller hsp40 proteins, ATP-bound hsp70 molecules grasp their target protein and then hydrolyze ATP to ADP, undergoing conformational changes. These proteins recognize a small stretch of hydrophobic amino acids on a protein’s surface. They share an affinity for the exposed hydrophobic patches on incompletely folded proteins. The heat shock proteins bind and release polypeptides in a cycle involving several other proteins (including a class called Hsp40) and ATP hydrolysis. Some chaperones also facilitate the quaternary assembly of oligomeric proteins. They also block the folding of some proteins that remains unfolded until they have been translocated across membranes. They have indirect action of binding and stabilizing the unfolded or partly folded proteins that preventing these proteins from aggregation and degradation. The hsp70 machinery acts early in the life of many proteins (often before the protein leaves the ribosome. These proteins are more abundant in cells stressed by elevated temperatures such that named as heat shock protein. 1.The first class, a family of proteins called Hsp70.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
